Basal Cell Carcinoma: Essential Guide for Optometrists
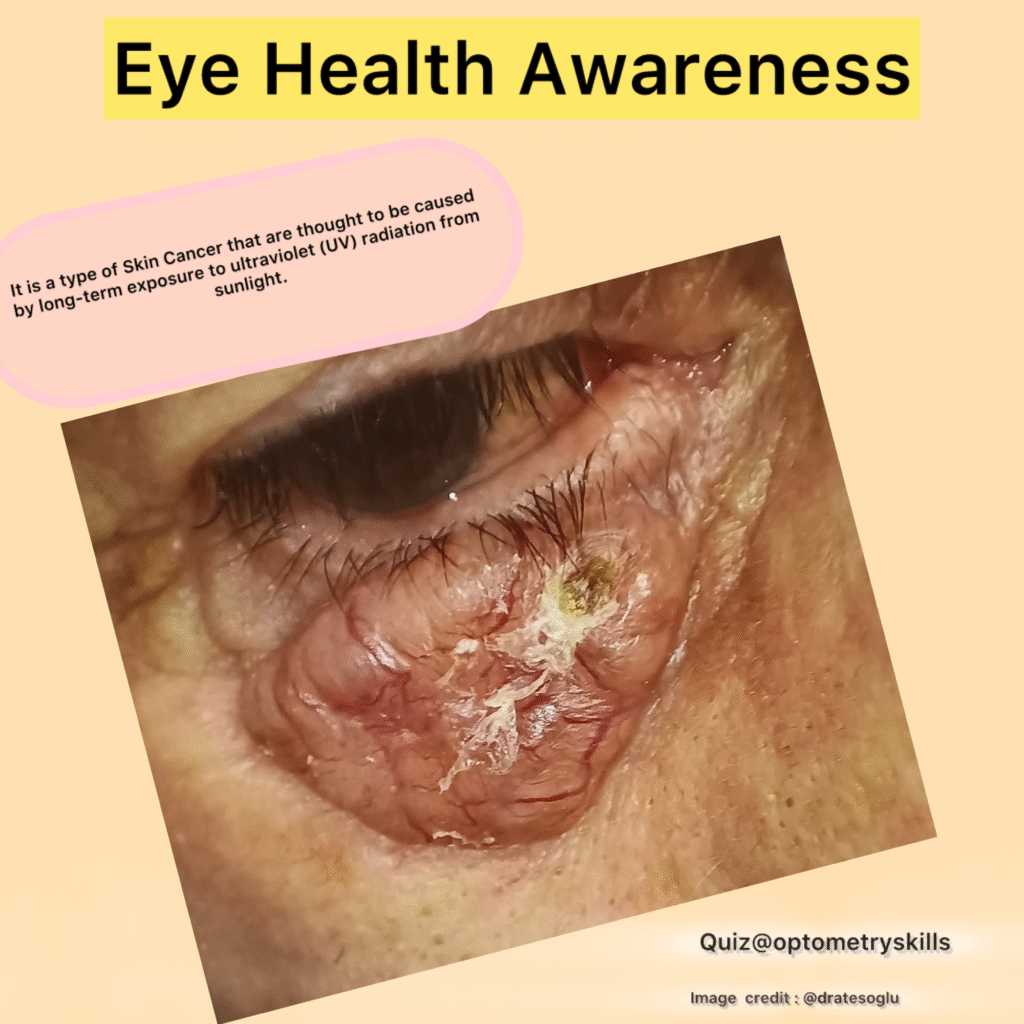
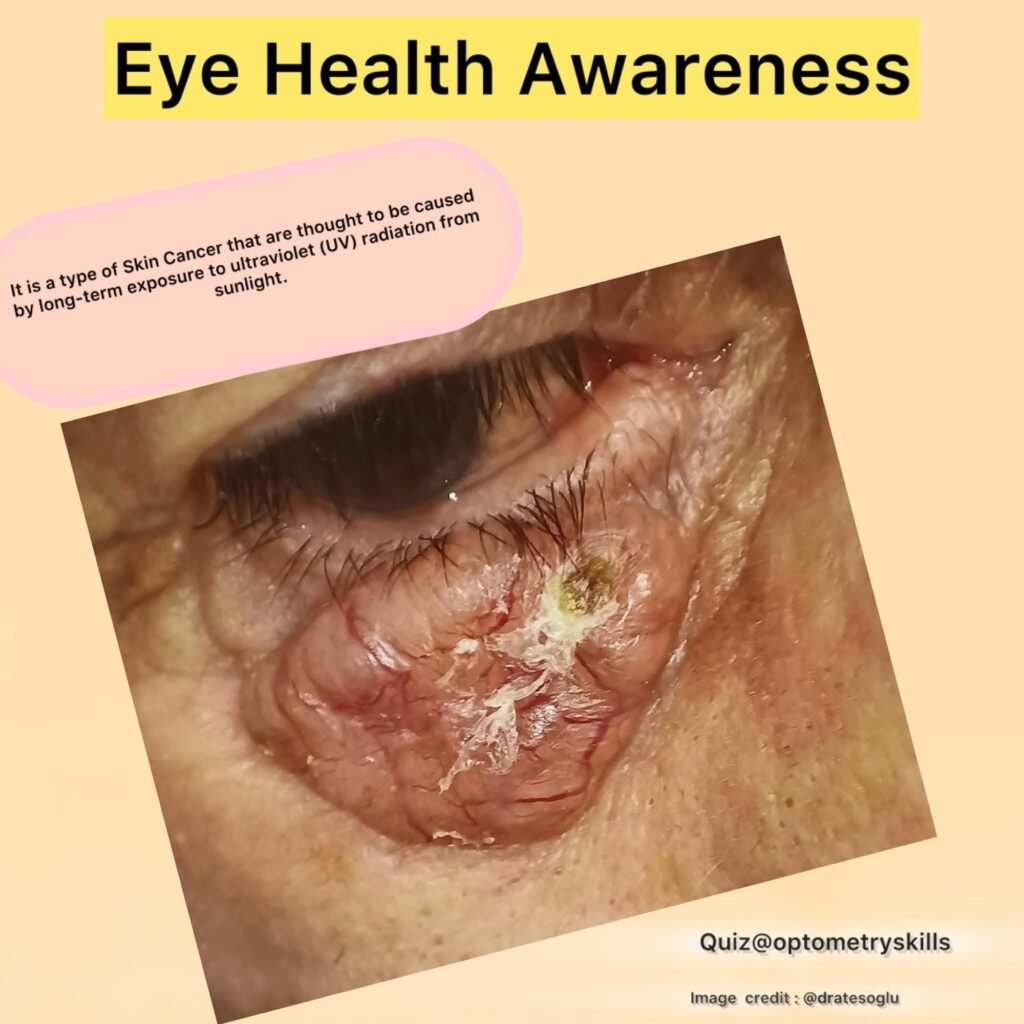
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC) is the most common type of skin cancer and the most frequent malignant tumor of the eyelid. Though BCC rarely metastasizes, it can cause significant local tissue destruction, including invasion of ocular structures. Early identification by optometrists is crucial to prevent vision loss and disfigurement.
Common Sites of BCC in the Ocular Region
Lower eyelid (most common, ~50-60% of cases) Medial canthus Upper eyelid Lateral canthus
Clinical Features of BCC
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Pearly, translucent nodule with rolled edges |
| Surface Features | Telangiectatic vessels, possible ulceration |
| Growth Pattern | Slow-growing but locally invasive |
| Symptoms | Often asymptomatic; later stages may cause irritation, bleeding, or vision changes |
| Advanced Features | Central ulceration (rodent ulcer), lash loss, distortion of eyelid margin |
Symptoms
Often asymptomatic; later stages may cause irritation, bleeding, or vision changes
Advanced Features
Central ulceration (rodent ulcer), lash loss, distortion of eyelid margin
Risk Factors
Chronic sun exposure (UV radiation) Fair skin and light-colored eyes Older age Personal or family history of skin cancers Immunosuppression History of radiation exposure
Optometric Management
1. Assessment
Perform a detailed external examination of periocular skin. Use slit-lamp magnification to assess lesion edges, surface, and vascularity. Look for associated signs: madarosis (lash loss), lid notching, or ulceration.
2. Documentation
Capture high-quality external photographs at baseline. Document lesion size, location, texture, and any changes over time.
3. Referral Guidelines
Urgent Referral to oculoplastics or dermatology if: Suspicious appearance (pearly nodule, telangiectasia, ulceration) Progressive growth Eyelid margin distortion Lash loss
BCC is confirmed through biopsy, with treatment often involving surgical excision (Mohs micrographic surgery preferred).
Role of Optometrists After Referral
Monitor for recurrence during routine eye exams. Educate patients on UV protection (wide-brim hats, UV-blocking sunglasses). Reinforce regular skin cancer screenings, especially in high-risk individuals.
Quick Reference Summary
✅ Suspect BCC with pearly nodules, telangiectasia, or ulceration
✅ Always document and photograph suspicious lesions
✅ Refer promptly to oculoplastics or dermatology
✅ Emphasize UV protection and follow-up care
Conclusion
Optometrists have a pivotal role in the early detection of basal cell carcinoma, especially in the periocular region. Recognizing typical features and knowing when to refer can prevent serious ocular complications and improve patient outcomes.
Follow us in Facebook for Daily Eye care Discussion
