Index
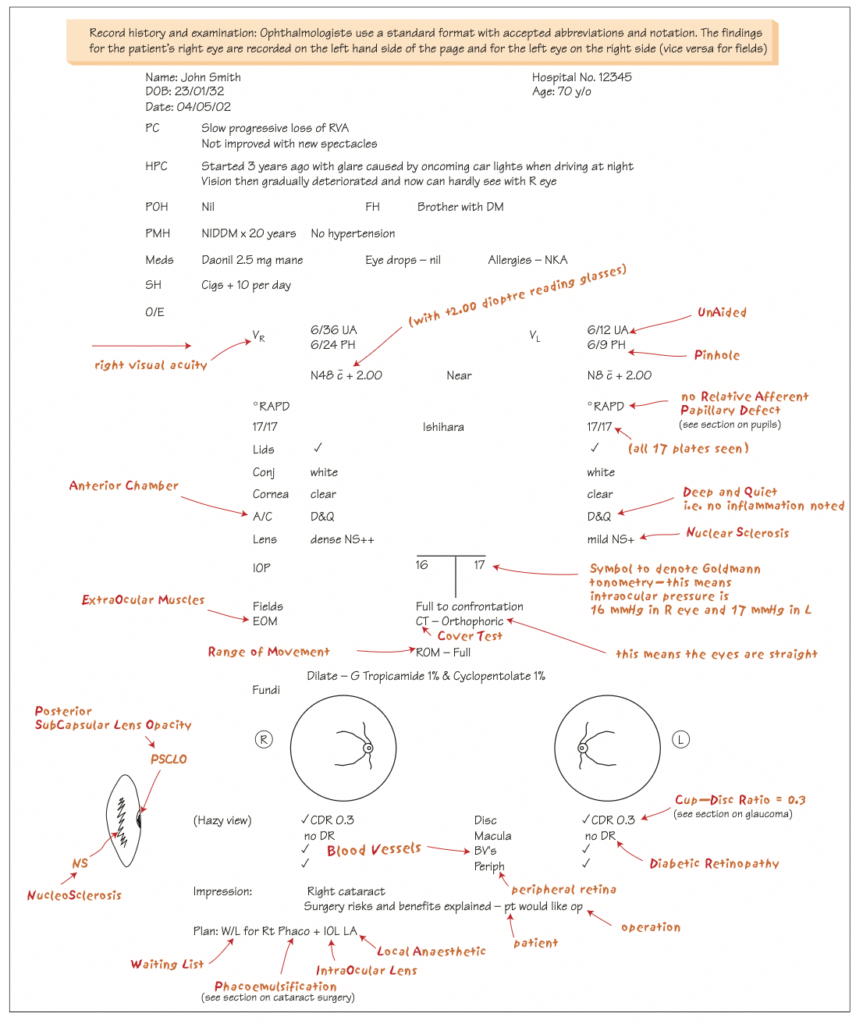
Record History and Examination in Ophthalmology
Read about the standard format ophthalmologists use for recording patient history and examination, including accepted abbreviations, notation conventions, and a detailed case example illustrating how findings are documented.
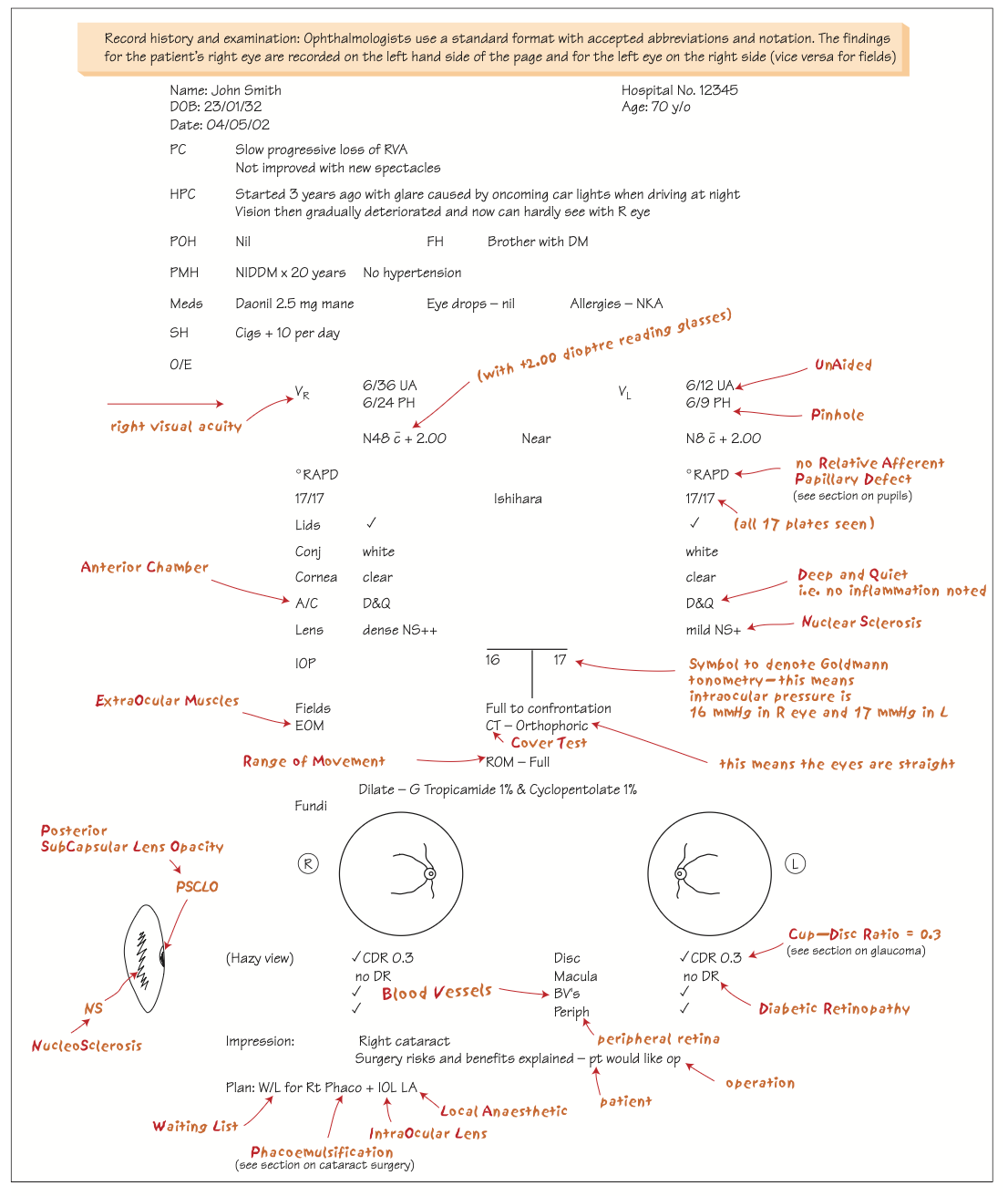
Image is taken from book : Ophthalmology at a glance (Amazon)
Summary of Common Ophthalmic Abbreviations Used
| Abbreviation | Meaning |
|---|---|
| PC | Presenting Complaint |
| HPC | History of Presenting Complaint |
| POH | Past Ocular History |
| PMH | Past Medical History |
| FH | Family History |
| SH | Social History |
| VA | Visual Acuity |
| UA | Unaided |
| PH | Pinhole |
| NIDDM | Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus |
| RAPD | Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect |
| NS | Nuclear Sclerosis |
| PSCLO | Posterior Subcapsular Lens Opacity |
| IOP | Intraocular Pressure |
| CDR | Cup-Disc Ratio |
| DR | Diabetic Retinopathy |
| LA | Local Anaesthetic |
| IOL | Intraocular Lens |
| W/L | Waiting List |
Ophthalmic Record and Examination Checklist
1. Patient Details
- Name
- Date of birth (DOB)
- Age
- Date of examination
- Hospital/Clinic number
- Contact information (if required)
2. Presenting Complaint (PC)
- Main reason for visit (in patient’s own words)
- Duration and nature of symptoms
- Whether one or both eyes are affected
3. History of Presenting Complaint (HPC)
- Onset (sudden or gradual)
- Duration and progression
- Associated symptoms (pain, glare, redness, floaters, flashes, diplopia, etc.)
- Any precipitating or relieving factors
- Impact on daily activities (e.g., driving, reading, glare at night)
4. Past Ocular History (POH)
- Previous eye diseases (glaucoma, cataract, trauma, uveitis, etc.)
- Previous surgeries or laser treatments
- History of spectacles or contact lens use
- Any use of topical medications
5. Family History (FH)
- Eye diseases in family (e.g., glaucoma, retinitis pigmentosa, diabetic retinopathy)
- Systemic diseases (e.g., diabetes, hypertension)
6. Past Medical History (PMH)
- Systemic conditions (e.g., diabetes, hypertension, thyroid disease, autoimmune disorders)
- Duration and treatment
- Any recent hospital admissions
7. Medications
- Current systemic medications
- Any eye drops or ointments
- Over-the-counter medications or supplements
8. Allergies
- Drug allergies
- Latex, preservatives, or contact lens solution allergies
- Reaction details if known
9. Social History (SH)
- Smoking (amount and duration)
- Alcohol consumption
- Occupation (especially if visual demand or risk of eye trauma is high)
- Driving status
- Use of visual display units (screens)
10. Examination (O/E)
a. Visual Acuity (VA)
- Distance Vision: Unaided, with spectacles, and with pinhole
- Near Vision: With and without correction
- Notation: Snellen or LogMAR chart
b. Pupils
- Size, shape, and reaction to light (direct and consensual)
- Check for Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect (RAPD)
c. Colour Vision
- Ishihara plates or other colour tests
d. External Examination
- Lids and lashes
- Conjunctiva and sclera
- Cornea (clarity, surface)
- Anterior chamber depth and activity (cells/flare)
- Iris (pattern, colour, abnormalities)
- Lens (clarity, presence of cataract)
e. Intraocular Pressure (IOP)
- Measure by Goldmann Applanation or other tonometer
- Record readings for each eye
f. Ocular Motility
- Extraocular muscle movement (EOM)
- Cover test (for strabismus/orthophoria)
- Range of movement (ROM)
- Diplopia charting if needed
g. Visual Fields
- Confrontation test (gross field defects)
- Automated perimetry if indicated
h. Fundus Examination (Posterior Segment)
- Optic Disc: colour, margins, cup-disc ratio (CDR)
- Macula: reflex, edema, pigmentation, drusen
- Retinal Vessels: calibre, tortuosity, hemorrhages, exudates
- Periphery: retinal tears, detachments, degenerations
11. Special Tests (as indicated)
- Slit-lamp biomicroscopy
- Gonioscopy
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
- Fundus photography
- Visual field testing
- Amsler grid (for macular function)
12. Diagnosis / Impression
- Summary of findings
- Primary and differential diagnoses
13. Management Plan
- Further investigations (if any)
- Treatment prescribed (medical or surgical)
- Patient counselling
- Follow-up date and instructions
14. Documentation Notes
- Signature and designation of examiner
- Date and time of entry
- Ensure right eye (OD) findings are recorded on the left side, and left eye (OS) on the right side of the examination page
If you like our post, Consider Sharing in your Social Media. Thanks. Follow our Page Optometrykills in Facebook for Daily Clinical Pearls.
